The justify-items property defines the default justify-self for all child boxes, giving them all a default way of justifying each box along the appropriate axis.
The justify-items property has gained use with the introduction of Flexbox and Grid layouts, but is also applies to:
- absolutely-positioned boxes
- block-level boxes
- static-position of absolutely positioned boxes
- table cells
| Initial Value | legacy |
| Applies to | All elements. |
| Inherited | No. |
| Animatable | No. |
| Version | CSS3 |
| DOM Syntax | object.style.justifyItems = "start"; |
Syntax
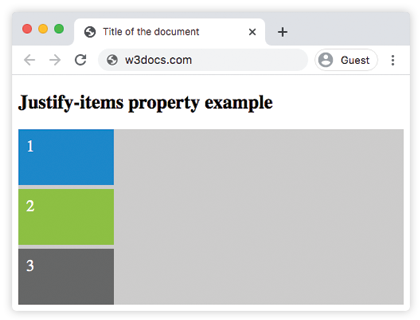
justify-items: auto | normal | start | end | flex-start | flex-end | self-start | self-end | center | left | right | baseline | first baseline | last baseline | stretch | safe | unsafe | legacy | initial | inherit;Example of the justify-items property:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title of the document</title>
<style>
#example {
display: grid;
grid-template-columns: 1fr;
grid-template-rows: 1fr 1fr 1fr;
grid-gap: 5px;
justify-items: start;
background-color: #cccccc;
}
#example > div {
padding: 10px;
font-size: 20px;
color: white;
width: 100px;
height: 50px;
}
.one {
background-color: #1c87c9;
}
.two {
background-color: #8ebf42;
}
.three {
background-color: #666666;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h2>Justify-items property example</h2>
<div id="example">
<div class="one">1</div>
<div class="two">2</div>
<div class="three">3</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>Result
Example of the justify-items property with the "center" value:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title of the document</title>
<style>
#example {
display: grid;
grid-template-columns: 1fr;
grid-template-rows: 1fr 1fr 1fr;
grid-gap: 5px;
justify-items: center;
background-color: #cccccc;
}
#example > div {
padding: 10px;
font-size: 20px;
color: white;
width: 100px;
height: 50px;
}
.one {
background-color: #1c87c9;
}
.two {
background-color: #8ebf42;
}
.three {
background-color: #666666;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h2>Justify-items property example</h2>
<div id="example">
<div class="one">1</div>
<div class="two">2</div>
<div class="three">3</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>Example of the justify-items property with the "first baseline" value:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title of the document</title>
<style>
.container {
display: grid;
padding-top: 10px;
height: 250px;
grid-template-columns: 1fr 1fr 1fr;
grid-template-rows: auto;
background: #ccc;
justify-items: first baseline;
}
.item {
width: 50%;
height: 50%;
text-align: center;
}
.item1 {
background: red;
}
.item2 {
background: blue;
}
.item3 {
background: green;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h2>Justify-items property example</h2>
<div class="container">
<div class="item1 item">1</div>
<div class="item2 item">2</div>
<div class="item3 item">3</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>Example of the justify-items property with the "self-end" value:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title of the document</title>
<style>
#example {
display: grid;
grid-template-columns: 1fr;
grid-template-rows: 1fr 1fr 1fr;
grid-gap: 5px;
justify-items: self-end;
background-color: #cccccc;
}
#example > div {
padding: 10px;
font-size: 20px;
color: white;
width: 100px;
height: 50px;
}
.one {
background-color: #1c87c9;
}
.two {
background-color: #8ebf42;
}
.three {
background-color: #666666;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h2>Justify-items property example</h2>
<div id="example">
<div class="one">1</div>
<div class="two">2</div>
<div class="three">3</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>Values
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| auto | If the box has no parent, or is absolutely positioned, the auto value represents normal. |
| normal |
The effect of this value depends on the layout mode:
|
| start | All elements are positioned against each other on the starting (left) edge of the container. |
| end | All elements are positioned against each other on the ending (right) edge of the container. |
| flex-start | Items are placed at the beginning of the container. |
| flex-end | Items are placed at the end of the container. |
| self-start | Item is allowed to place itself on the container edge based on its own starting side. |
| self-end | Item is allowed to place itself on the container edge based on its own ending side. |
| center | Items are positioned next to each other toward the center of the container. |
| left | Items are placed next to each other toward the left side of the container. If the property’s axis is not parallel with the inline axis, this value behaves like end. |
| right | Items are placed next to each other toward the right side of the container. If the property’s axis is not parallel with the inline axis, this value behaves like start. |
| baseline first-baseline last-baseline | Aligns all elements within a group by matching up their alignment baselines. |
| stretch | Stretch the element to both edges of the container vertically and horizontally to fit the container. |
| safe | If the size of the item overflows the alignment container, the item is aligned as if the alignment mode is start. |
| unsafe | Regardless of the item’s size and alignment container, the alignment value is honored. |
| legacy | Makes the value inherited by the box descendants. |
| initial | It makes the property use its default value. |
| inherit | It inherits the property from its parents element. |
Browser support
|
|
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
29.0 21.0 -webkit- |
11+ |
28.0 18.0 -moz- |
9.0 6.1-webkit- | 17+ |
Practice Your Knowledge
What does the CSS 'justify-items' property do?
Correct!
Incorrect!
Quiz Time: Test Your Skills!
Ready to challenge what you've learned? Dive into our interactive quizzes for a deeper understanding and a fun way to reinforce your knowledge.