The <link> tag sets the relationship between the current document and the external resource. It is generally used to link to the external CSS stylesheet.
The <link> tag can be used to link different versions of a page. This is useful if there are several translations of content.
An HTML document can have several <link> elements for loading different types of script or page. All these <link> elements should be placed in the <head> section of the document (commonly before the closing </head> tag), and they can be used many times.
Syntax
The <link> tag is empty, which means that the closing tag isn’t required. It contains only attributes. But in XHTML, the (<link>) tag must be closed (<link/>).
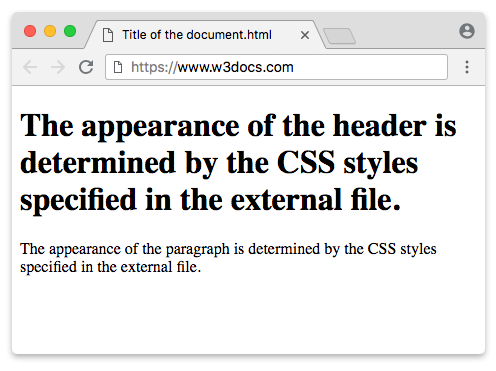
Example of the HTML <link> tag:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="style.css">
</head>
<body>
<h1>The appearance of the header is determined by the CSS styles specified in the external file.</h1>
<p>The appearance of the paragraph is determined by the CSS styles specified in the external file.</p>
</body>
</html>Result
Attributes
| Attribute | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| charset | char_encoding | Defines the coding of the linked document. Not supported in HTML5. |
| href | URL | Defines the URL of the external file. |
| hreflang | language_code | Defines the text language of the linked document. |
| media | media_query | Defines the device, for which the styles will be applied. |
| rel | alternate archives author bookmark external first help icon last license next nofollow noreferrer pingback prefetch prev search sidebar stylesheet tag up |
Defines the relationship between the current document and the linked file. |
| rev | reversed relationship | Defines the relationship between the current and linked documents. Not supported in HTML5. |
| sizes | HeightxWeight | Sets the size of associated icons. Used only with rel = "icon". |
| target | Defines how the link should be opened: | |
| _blank | In a new window. | |
| _self | In the current window. | |
| _top | To the full width of the window. | |
| _parent | In the parent frame. | |
| frame_name | In the frame. Not supported in HTML5. |
|
| type | media_type | Defines the MIME-type (specification for network transfer of various types of files) of the linked document. |
The <link>tag also supports Global Attributes and the Event Attributes.
Browser support
|
|
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
Practice Your Knowledge
Quiz Time: Test Your Skills!
Ready to challenge what you've learned? Dive into our interactive quizzes for a deeper understanding and a fun way to reinforce your knowledge.