How to Delete Commits from a Branch in Git
This is a useful guide that will help you to delete commits from a branch in Git, accurately. To delete commits in Git, follow the steps below.
Deleting the latest commits
Generally, the git reset command is used for deleting the latest commits in Git.
Deleting the most recent commit
To delete the most recent commit, run the command below:
git reset --hard HEAD~1Note that HEAD~1 means one commit prior to the HEAD.
Deleting multiple latest commits
To delete the N-th latest commits, you should use HEAD~N as the argument of git reset.
git reset --hard HEAD~NAs an alternative to this method, you can select the appropriate commit by its hash instead of HEAD~N. Here is how to do it:
git reset --hard <sha1-commit-hash>Deleting a Commit in the Middle of the History
Undoing the Changes of the "Middle" Commit
There exists a safe way of deleting a commit in the middle of the history: using the git revert command. It adds a new commit, which undoes everything the middle commit has changed.
git revert <sha1-commit-hash>Deleting the "Middle" Commit from the History.
Take into account that git revert doesn't delete the middle commit. If you want to delete it from the history, then run git rebase in interactive mode:
git rebase -i <sha1-commit-hash>Then, an editor opens that shows up the commits following the one you have selected. It will offer you to input the command for each commit. All you need to do is typing "drop" at the beginning of each commit you want to delete.
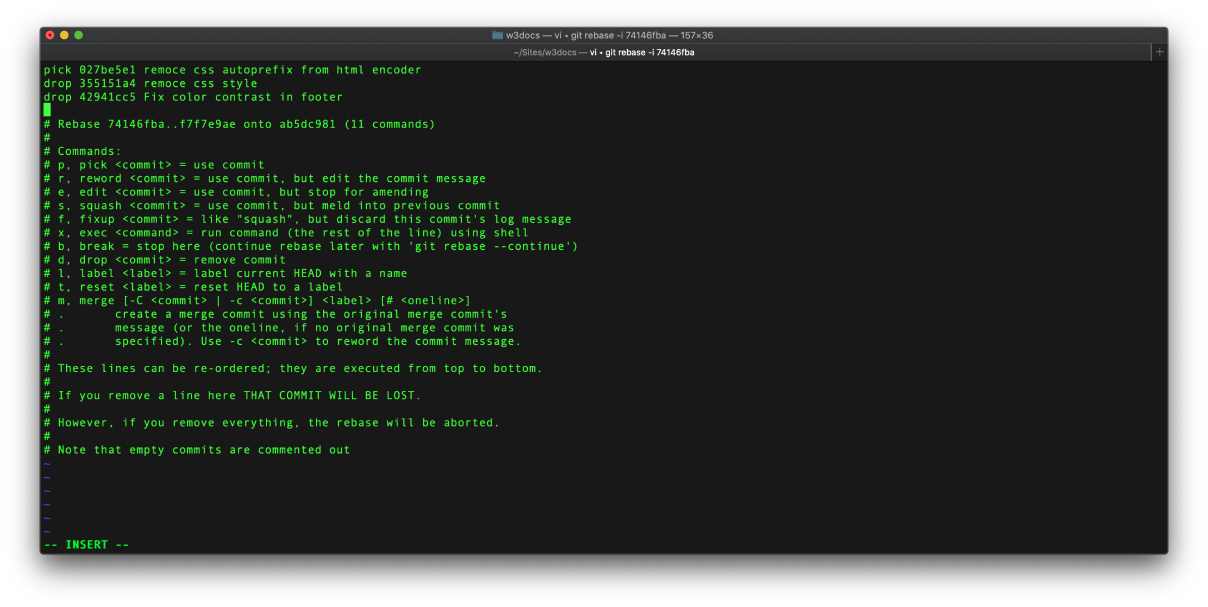
Pushing changes
In case you have already pushed your commits, then you need to run git push with the --force flag to delete the commits from the remote (suppose, the name of remote is origin, which is by default):
git push origin HEAD --forceHere is an alternative and safer way to push combined commits:
git push --force-with-lease origin HEADFinding the deleted commit
Finally, in case you want to find the deleted commit, you can do it with the help of the git reflog command:
git reflogHow git reset Works
The git reset command is a powerful tool for undoing changes.
Git reset has some similarities with the git checkout command because both of the commands work on HEAD. Git checkout operates only on HEAD reference pointer, and git reset passes that HEAD reference pointer and present branch reference pointer.
How git reflog Works
This command is generally used for recording updates made to the branches. With the help of the git reflog command, you can return to the commits even to those that have not been referenced by any branch of tag. Reflog contains information about the preceding state of branches and allows returning to that state if needed.
How git rebase Works
The git rebase command is aimed at integrating changes from a branch to another. It is used as an alternative to the git merge command. However, there is a notable difference between these two commands: git rebase rewrites the commit history for creating a more linear project history. There are two modes of git rebase command: standard and interactive. In standard mode git rebase will automatically apply the commits in the current working branch to the passed branch’s head. The current branch will be rebased onto <base> .